2.3 KiB
DJI Gimbal Retro-Engineering
The aim of this project is to be able to use the 3-axis DJI gimbal with a custom open source controller. This high quality gimbal is very tiny and easy to find as replacement part which makes it very suitable for DIY projects.
Description
todo
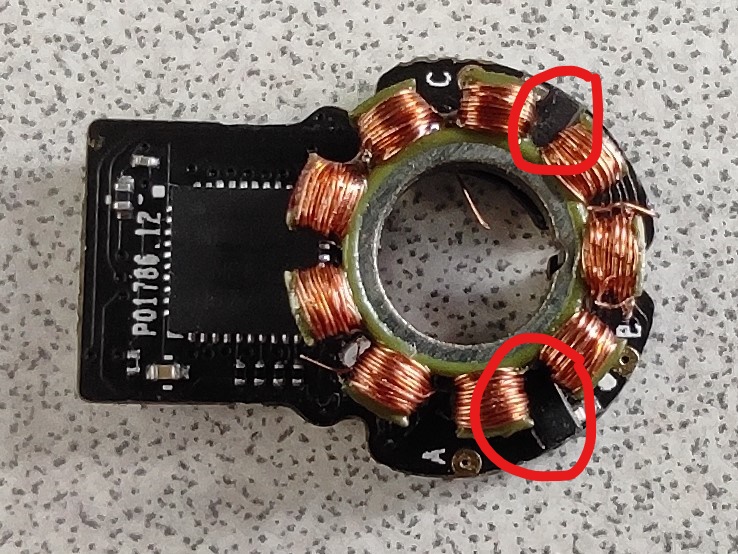
Pinout identification
The Gimbal is composed of a flex PCB with a main connector and 3 smaller for each motor. The main end connector is a 40-pin mezzanine board to board connectors. In order to work easily I have designed a breakout board which open to a 2.54" header. Here is the strategy I followed to find the pinout:
- Find all equipotential pins: With a multimeter set to continuity tests, and test all the combinations
- Group remaining pins by motor With the multimeter find all the pins connected to the motor connector. (Reapeat 3 times)
Open-loop control
Each motor has its own drivers a MP6536. Which makes it easy as no additional hardware is necessary to drive the motors. There are 4 pins from the MP6536:
- PWM1
- PWM2
- PWM3
- Fault : Output. When low, indicates overtemperature, over-current, or under-voltage.
Connected directly to a MCU and with the Simple FOC Library, open-loop control works quite well. However due to open-loop control, it cannot know when a "step" is missed so misalignment can occur. Also, the motor tends to become quite hot due to the continuous current sent to the coils.
Position estimation with the integrated linear hall sensors
1. Setup
Each motor is composed of two ratiometric linear hall sensors. (Texas Instrument DRV5053 Analog-Bipolar Hall Effect Sensor) They are placed at around 120º from each other (eyes measured) and measure the magnetic field of the rotor.
Ratiometric means that the output signal is proportional to the voltage supply to the sensor. In this setup, with 5V supply, the output measured is between 520mV and 1.5V, so a 1V amplitude.
2. Measures
These oscilloscope traces are the sensor output when rotating the rotor forth and back. (a bit less than 180º on the 3rd motor)
The channel 0 (Yellow) is the Hall 1 and the Channel 1 (Green) is the Hall 2
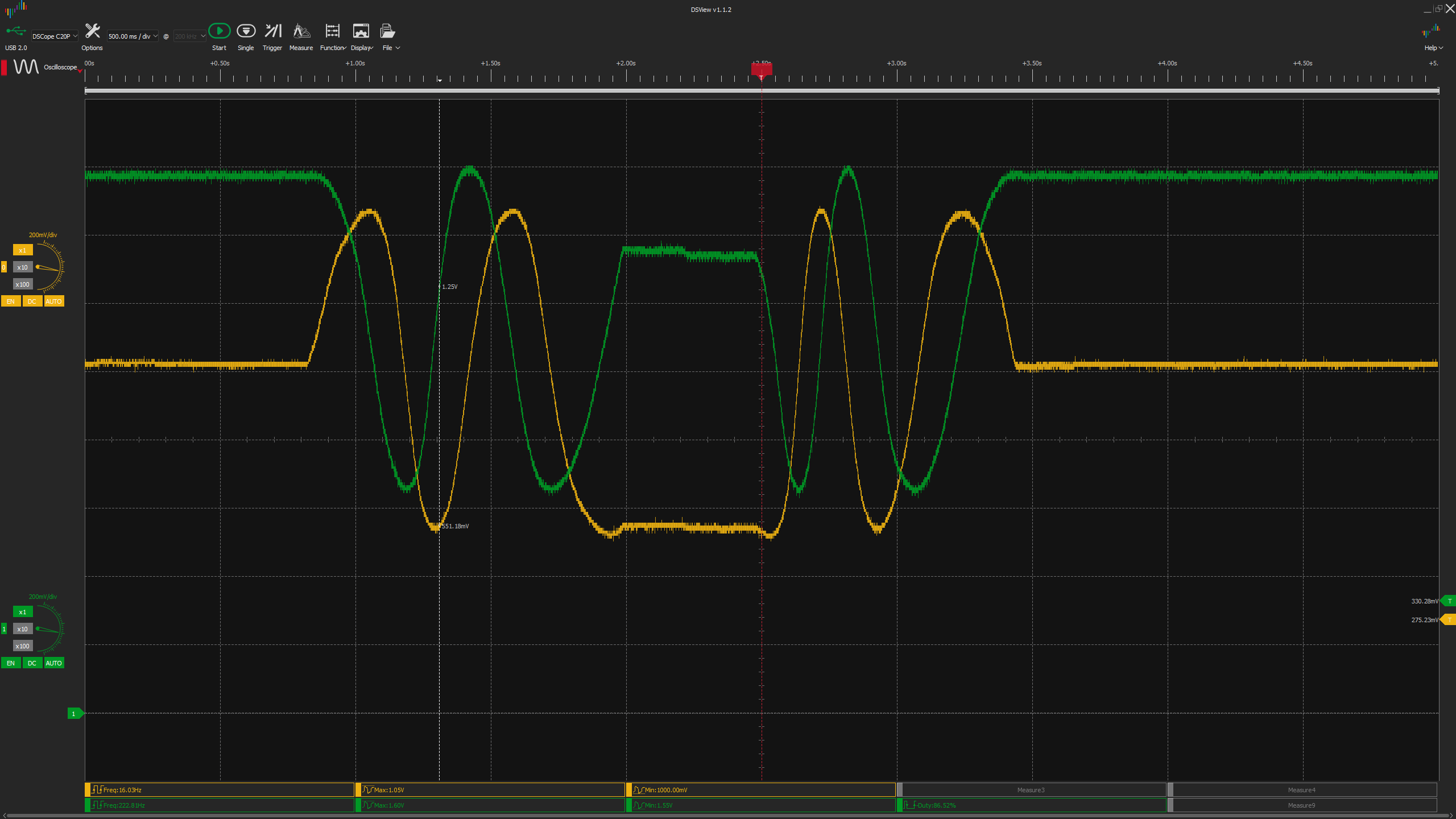
3. Analysis
We can see that in the first movement (positive rotation), the green is out of phase and opposite